Policies
Everything in OpenBao is path-based, and policies are no exception. Policies provide a declarative way to grant or forbid access to certain paths and operations in OpenBao. This section discusses policy workflows and syntaxes.
Policies are deny by default, so an empty policy grants no permission in the system.
Policy-authorization workflow
Before a human or machine can gain access, an administrator must configure OpenBao with an auth method. Authentication is the process by which human or machine-supplied information is verified against an internal or external system.
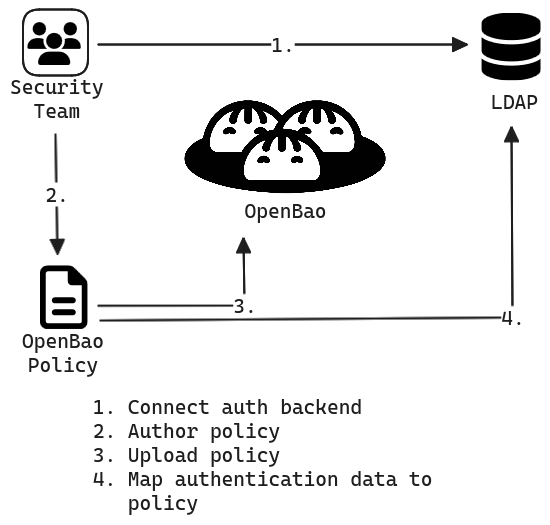
Consider the following diagram, which illustrates the steps a security team would take to configure OpenBao to authenticate using a corporate LDAP or ActiveDirectory installation. Even though this example uses LDAP, the concept applies to all auth methods.
-
The security team configures OpenBao to connect to an auth method. This configuration varies by auth method. In the case of LDAP, OpenBao needs to know the address of the LDAP server and whether to connect using TLS. It is important to note that OpenBao does not store a copy of the LDAP database - OpenBao will delegate the authentication to the auth method.
-
The security team authors a policy (or uses an existing policy) which grants access to paths in OpenBao. Policies are written in HCL in your editor of preference and saved to disk.
-
The policy's contents are uploaded and stored in OpenBao and referenced by name. You can think of the policy's name as a pointer or symlink to its set of rules.
-
Most importantly, the security team maps data in the auth method to a policy. For example, the security team might create mappings like:
Members of the OU group "dev" map to the OpenBao policy named "readonly-dev".
or
Members of the OU group "ops" map to the OpenBao policies "admin" and "auditor".
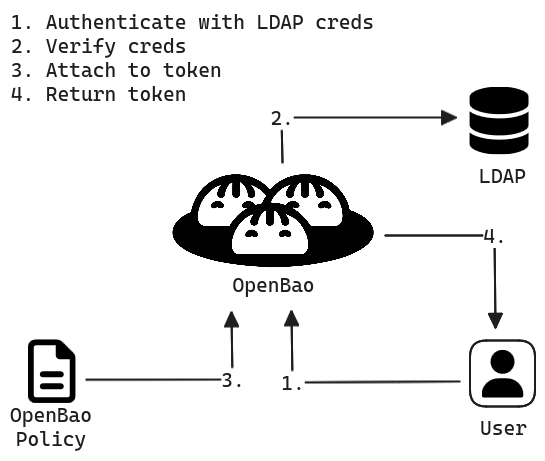
Now OpenBao has an internal mapping between a backend authentication system and internal policy. When a user authenticates to OpenBao, the actual authentication is delegated to the auth method. As a user, the flow looks like:
-
A user attempts to authenticate to OpenBao using their LDAP credentials, providing OpenBao with their LDAP username and password.
-
OpenBao establishes a connection to LDAP and asks the LDAP server to verify the given credentials. Assuming this is successful, the LDAP server returns the information about the user, including the OU groups.
-
OpenBao maps the result from the LDAP server to policies inside OpenBao using the mapping configured by the security team in the previous section. OpenBao then generates a token and attaches the matching policies.
-
OpenBao returns the token to the user. This token has the correct policies assigned, as dictated by the mapping configuration that was setup by the security team in advance.
The user then uses this OpenBao token for future operations. If the user performs the authentication steps again, they will get a new token. The token will have the same permissions, but the actual token will be different. Authenticating a second time does not invalidate the original token.
Policy syntax
Policies are written in HCL or JSON and describe which paths in OpenBao a user or machine is allowed to access.
Here is a very simple policy which grants read capabilities to the KVv1 path
"secret/foo":
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
Equivalently in JSON, this would be:
{
"path": {
"secret/foo": {
"capabilities": ["read"]
}
}
}
When this policy is assigned to a token, the token can read from "secret/foo".
However, the token cannot update or delete "secret/foo", since the
capabilities do not allow it. Because policies are deny by default, the
token would have no other access in OpenBao.
Here is a more detailed policy, and it is documented inline:
# This section grants all access on "secret/*". further restrictions can be
# applied to this broad policy, as shown below.
path "secret/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "read", "update", "patch", "delete", "list", "scan"]
}
# Even though we allowed secret/*, this line explicitly denies
# secret/super-secret. this takes precedence.
path "secret/super-secret" {
capabilities = ["deny"]
}
# Policies can also specify allowed, disallowed, and required parameters. here
# the key "secret/restricted" can only contain "foo" (any value) and "bar" (one
# of "zip" or "zap").
path "secret/restricted" {
capabilities = ["create"]
allowed_parameters = {
"foo" = []
"bar" = ["zip", "zap"]
}
}
Policies use path-based matching to test the set of capabilities against a
request. A policy path may specify an exact path to match, or it could specify
a glob pattern which instructs OpenBao to use a prefix match:
# Permit reading only "secret/foo". an attached token cannot read "secret/food"
# or "secret/foo/bar".
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
# Permit reading everything under "secret/bar". an attached token could read
# "secret/bar/zip", "secret/bar/zip/zap", but not "secret/bars/zip".
path "secret/bar/*" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
# Permit reading everything prefixed with "zip-". an attached token could read
# "secret/zip-zap" or "secret/zip-zap/zong", but not "secret/zip/zap
path "secret/zip-*" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
In addition, a + can be used to denote any number of characters bounded
within a single path segment:
# Permit reading the "teamb" path under any top-level path under secret/
path "secret/+/teamb" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
# Permit reading secret/foo/bar/teamb, secret/bar/foo/teamb, etc.
path "secret/+/+/teamb" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
OpenBao's architecture is similar to a filesystem. Every action in OpenBao has a
corresponding path and capability - even OpenBao's internal core configuration
endpoints live under the "sys/" path. Policies define access to these paths and
capabilities, which controls a token's access to credentials in OpenBao.
Note: The policy rules that OpenBao applies are determined by the most-specific match available, using the priority rules described below. This may be an exact match or the longest-prefix match of a glob. If the same pattern appears in multiple policies, we take the union of the capabilities. If different patterns appear in the applicable policies, we take only the highest-priority match from those policies.
This means if you define a policy for "secret/foo*", the policy would
also match "secret/foobar". Specifically, when there are potentially multiple
matching policy paths, P1 and P2, the following matching criteria is applied:
- If the first wildcard (
+) or glob (*) occurs earlier inP1,P1is lower priority - If
P1ends in*andP2doesn't,P1is lower priority - If
P1has more+(wildcard) segments,P1is lower priority - If
P1is shorter, it is lower priority - If
P1is smaller lexicographically, it is lower priority
For example, given the two paths, "secret/*" and "secret/+/+/foo/*", the first
wildcard appears in the same place, both end in * and the latter has two wildcard
segments while the former has zero. So we end at rule (3), and give "secret/+/+/foo/*"
lower priority.
Informational: The glob character referred to in this documentation is the
asterisk (*). It is not a regular expression and is only supported as the
last character of the path!
When providing list or scan capabilities, it is important to note that
since listing always operates on a prefix, policies must operate on a prefix
because OpenBao will sanitize request paths to be prefixes.
Capabilities
Each path must define one or more capabilities which provide fine-grained control over permitted (or denied) operations. As shown in the examples above, capabilities are always specified as a list of strings, even if there is only one capability.
To determine the capabilities needed to perform a specific operation, the -output-policy flag can be added to the CLI subcommand. For an example, refer to the Print Policy Requirements document section.
The list of capabilities include the following:
-
create(POST/PUT) - Allows creating data at the given path. Very few parts of OpenBao distinguish betweencreateandupdate, so most operations require bothcreateandupdatecapabilities. Parts of OpenBao that provide such a distinction are noted in documentation. -
read(GET) - Allows reading the data at the given path. -
update(POST/PUT) - Allows changing the data at the given path. In most parts of OpenBao, this implicitly includes the ability to create the initial value at the path. -
patch(PATCH) - Allows partial updates to the data at a given path. -
delete(DELETE) - Allows deleting the data at the given path. -
list(LIST) - Allows listing values at the given path. Note that the keys returned by alistoperation are not filtered by policies. Do not encode sensitive information in key names. Not all backends support listing. -
scan(SCAN) - Allows recursively listing ("scanning") values at the given path. Note that the keys returned by alistoperation are not filtered by policies. Do not encode sensitive information in key names. Not all backends support listing.
In the list above, the associated HTTP verbs are shown in parenthesis next to the capability. When authoring policy, it is usually helpful to look at the HTTP API documentation for the paths and HTTP verbs and map them back onto capabilities. While the mapping is not strictly 1:1, they are often very similarly matched.
In addition to the standard set, there are some capabilities that do not map to HTTP verbs.
-
sudo- Allows access to paths that are root-protected. Tokens are not permitted to interact with these paths unless they have thesudocapability (in addition to the other necessary capabilities for performing an operation against that path, such asreadordelete).For example, modifying the audit log backends requires a token with
sudoprivileges. -
deny- Disallows access. This always takes precedence regardless of any other defined capabilities, includingsudo.
Note: Capabilities usually map to the HTTP verb, and not the underlying
action taken. This can be a common source of confusion. Generating database
credentials creates database credentials, but the HTTP request is a GET which
corresponds to a read capability. Thus, to grant access to generate database
credentials, the policy would grant read access on the appropriate path.
Templated policies
The policy syntax allows for doing variable replacement in some policy strings
with values available to the token. Currently identity information can be
injected, and currently the path keys in policies allow injection.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
identity.entity.id | The entity's ID |
identity.entity.name | The entity's name |
identity.entity.metadata.<metadata key> | Metadata associated with the entity for the given key |
identity.entity.aliases.<mount accessor>.id | Entity alias ID for the given mount |
identity.entity.aliases.<mount accessor>.name | Entity alias name for the given mount |
identity.entity.aliases.<mount accessor>.metadata.<metadata key> | Metadata associated with the alias for the given mount and metadata key |
identity.entity.aliases.<mount accessor>.custom_metadata.<custom_metadata key> | Custom metadata associated with the alias for the given mount and custom metadata key |
identity.groups.ids.<group id>.name | The group name for the given group ID |
identity.groups.names.<group name>.id | The group ID for the given group name |
identity.groups.ids.<group id>.metadata.<metadata key> | Metadata associated with the group for the given key |
identity.groups.names.<group name>.metadata.<metadata key> | Metadata associated with the group for the given key |
Examples
The following policy creates a section of the KVv2 Secret Engine to a specific user
path "secret/data/{{identity.entity.id}}/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "update", "patch", "read", "delete"]
}
path "secret/metadata/{{identity.entity.id}}/*" {
capabilities = ["list"]
}
If you wanted to create a shared section of KV that is associated with entities that are in a group.
# In the example below, the group ID maps a group and the path
path "secret/data/groups/{{identity.groups.ids.fb036ebc-2f62-4124-9503-42aa7A869741.name}}/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "update", "patch", "read", "delete"]
}
path "secret/metadata/groups/{{identity.groups.ids.fb036ebc-2f62-4124-9503-42aa7A869741.name}}/*" {
capabilities = ["list"]
}
Note: When developing templated policies, use IDs wherever possible. Each ID is unique to the user, whereas names can change over time and can be reused. This ensures that if a given user or group name is changed, the policy will be mapped to the intended entity or group.
If you want to use the metadata associated with an authentication plugin in your
templates, you will need to get its mount accessor and access it via the
aliases key.
You can get the mount accessor value using the following command:
$> bao auth list
Path Type Accessor Description
---- ---- -------- -----------
kubernetes/ kubernetes auth_kubernetes_xxxx n/a
token/ token auth_token_yyyy token based credentials
The following templated policy allows reading of the path associated with the Kubernetes service account namespace of the identity:
path "secret/data/{{identity.entity.aliases.auth_kubernetes_xxxx.metadata.service_account_namespace}}/*" {
capabilities = ["read"]
}
Fine-grained control
In addition to the standard set of capabilities, OpenBao offers finer-grained control over permissions at a given path. The capabilities associated with a path take precedence over permissions on parameters.
Each path can contain an optional, ignored field, comment which can be used
to describe the contents.
For instance:
path "pki/*" {
capabilities = ["deny"]
comment = "explicitly deny access to PKI path based on discussion in TRACKER-12345."
}
Path expiration
Specific paths in a policy can be set to automatically remove access at a point in time. This allows for lazy cleanup of policies: temporary access can be granted and long-term access guaranteed to be denied, without requiring cleanup and removal of the entire policy. When a policy is attached to an external authentication system's properties (e.g., LDAP groups or JWT claims) this is a useful additional control on top of expiring entire policies.
expiration(string: <optional>)- An optional expiration time for the given path, intime.RFC3339format.
For example:
path "secret/data/in-case-of-emergency" {
capabilities = ["read"]
expiration = "2006-01-02T15:04:05Z"
}
Parameter constraints
Note: The use of globs (*) may result in surprising or unexpected behavior.
Note: The allowed_parameters, denied_parameters, and required_parameters fields are not supported for policies used with the version 2 kv secrets engine.
See the API Specification for more information.
Policies can take into account HTTP request parameters to further constrain requests, using the following options:
-
required_parameters- A list of parameters that must be specified.# This requires the user to create "secret/profile" with a parameter/key named
# "name" and "id" where kv v1 is enabled at "secret/".
path "secret/profile" {
capabilities = ["create"]
required_parameters = ["name", "id"]
} -
allowed_parameters- A list of keys and values that are permitted on the given path.-
Setting a parameter with a value of the empty list allows the parameter to contain any value.
# This allows the user to update the password parameter value set on any
# users configured for userpass auth method. The password value can be
# anything. However, the user cannot update other parameter values such as
# token_ttl.
path "auth/userpass/users/*" {
capabilities = ["update"]
allowed_parameters = {
"password" = []
}
} -
Setting a parameter with a value of a populated list allows the parameter to contain only those values.
# This allows the user to create or update an encryption key for transit
# secrets engine enabled at "transit/". When you do, you can set the
# "auto_rotate_period" parameter value so that the key gets rotated.
# However, the rotation period must be "8h", "24h", or "5d". Any other value
# will result in an error.
path "transit/keys/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "update"]
allowed_parameters = {
"auto_rotate_period" = ["8h", "24h", "5d"]
}
} -
If any keys are specified, all non-specified parameters will be denied unless the parameter
"*"is set to an empty array, which will allow all other parameters to be modified. Parameters with specific values will still be restricted to those values.# When kv v1 secrets engine is enabled at "secret/", this allows the user to
# create "secret/foo" with a parameter named "bar". The parameter "bar" can
# only contain the values "zip" or "zap", but any other parameters may be
# created with any value.
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["create"]
allowed_parameters = {
"bar" = ["zip", "zap"]
"*" = []
}
}
-
-
denied_parameters- A list of keys and values that are not permitted on the given path. Any values specified here take precedence overallowed_parameters.-
Setting a parameter with a value of the empty list denies any changes to that parameter.
# This allows the user to update the userpass auth method's user
# configurations (e.g., "password") but cannot update the "token_policies"
# and "policies" parameter values.
path "auth/userpass/users/*" {
capabilities = ["update"]
denied_parameters = {
"token_policies" = []
"policies" = []
}
} -
Setting a parameter with a value of a populated list denies any parameter containing those values.
# This allows the user to create or update token roles. However, the
# "allowed_policies" parameter value cannot be "admin", but the user can
# assign any other policies to the parameter.
path "auth/token/roles/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "update"]
denied_parameters = {
"allowed_policies" = ["admin"]
}
} -
Setting to
"*"will deny any parameter.# This allows the user to create or update an encryption key for transit
# secrets engine enabled at "transit/". However, the user cannot set any of
# the configuration parameters. As a result, the created key will have all
# parameters set to default values.
path "transit/keys/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "update"]
denied_parameters = {
"*" = []
}
} -
If any parameters are specified, all non-specified parameters are allowed, unless
allowed_parametersis also set, in which case normal rules apply.
-
Parameter values also support prefix/suffix globbing. Globbing is enabled by
prepending or appending or prepending a splat (*) to the value:
# Only allow a parameter named "bar" with a value starting with "foo-*".
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["create"]
allowed_parameters = {
"bar" = ["foo-*"]
}
}
Note: the only value that can be used with the * parameter is [].
Parameter constraints limitations
Default values
Evaluation of policies with allowed_parameters, denied_parameters, and required_parameters happens
without consideration of parameters' default values.
Given the following policy:
# The "no_store" parameter cannot be false
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["create"]
denied_parameters = {
"no_store" = [false, "false"]
}
}
The following operation will error, because "no_store" is set to false:
$ bao write secret/foo no_store=false value=bar
Whereas the following operation will succeed, even if the "no_store" parameter must be a boolean, and it defaults to false:
# Succeeds because "no_store=false" isn't present in the parameters
$ bao write secret/foo value=bar
This is because the policy evaluator does not know what the default value is for the "no_store" parameter. All it sees is that the denied parameter isn't present in the command.
This can be resolved by requiring the "no_store" parameter in your policy:
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["create"]
required_parameters = ["no_store"]
denied_parameters = {
"no_store" = [false, "false"]
}
}
The following command, which previously succeeded, will now fail under the new policy because there is no "no_store" parameter:
$ bao write secret/foo value=bar
Globbing
It's also important to note that the use of globbing may result in surprising or unexpected behavior:
# This allows the user to create, update, or patch "secret/foo" with a parameter
# named "bar". the values passed to parameter "bar" must start with "baz/"
# so values like "baz/quux" are fine. however, values like
# "baz/quux,wibble,wobble,wubble" would also be accepted. the API that
# underlies "secret/foo" might allow comma delimited values for the "bar"
# parameter, and if it did, specifying a value like
# "baz/quux,wibble,wobble,wubble" would result in 4 different values getting
# passed along. seeing values like "wibble" or "wobble" getting passed to
# "secret/foo" might surprise someone that expected the allowed_parameters
# constraint to only allow values starting with "baz/".
path "secret/foo" {
capabilities = ["create", "update", "patch"]
allowed_parameters = {
"bar" = ["baz/*"]
}
}
Limiting pagination
The pagination_limit parameter allows policy authors to control the value of
limit on paginated list and scan endpoints. In conjunction with setting
required_parameters=["limit"] on the ACL policy, pagination becomes fully
required, rejecting the request if the client did not set limit; otherwise,
pagination is optional but, when limit is specified, the maximum number of
results is limited to the value of pagination_limit.
It is assumed that the policy author only sets pagination_limit on endpoints
conforming to the Paginated Lists RFC. This
allows the API to safely translate the value limit=max to a numerical value,
either limit=0 if no value was set or to the actual limit set by the policy
author.
Filtering list or scan results
By granting list or scan capabilities on a path, all results are returned
from the plugin, including entries which correlate to paths the token cannot
access. To filter these results, restricting them to only visible entries, use
the list_scan_response_keys_filter_path parameter. This parameter takes a
path containing a {{ .key }} template for which the line item is
substituted. When this key is an entry (without a trailing /), the path is
checked for read capability; when the key is a folder (with a trailing /),
this path is checked for list capability. The path of the list or scan
request is available via the {{ .path }} member. This path supports the
templating
helpers.
For example, restrict results in a KVv2 mount, based on whether the token can read the metadata:
path "test/metadata/*" {
capabilities = ["list", "scan"]
list_scan_response_keys_filter_path = "{{ .path }}{{ .key }}"
}
or on the ability to read the data:
path "test/metadata/*" {
capabilities = ["list", "scan"]
list_scan_response_keys_filter_path = "{{ .path | replace \"test/metadata/\" \"test/data/\" }}{{ .key }}"
}
We currently do not support this capability when policy evaluation for individual entries requires additional parameters; in this case, the list result may be completely empty.
Required response wrapping TTLs
These parameters can be used to set minimums/maximums on TTLs set by clients when requesting that a response be wrapped, with a granularity of a second. These use duration format strings.
In practice, setting a minimum TTL of one second effectively makes response wrapping mandatory for a particular path.
-
min_wrapping_ttl- The minimum allowed TTL that clients can specify for a wrapped response. In practice, setting a minimum TTL of one second effectively makes response wrapping mandatory for a particular path. It can also be used to ensure that the TTL is not too low, leading to end targets being unable to unwrap before the token expires. -
max_wrapping_ttl- The maximum allowed TTL that clients can specify for a wrapped response.
# This effectively makes response wrapping mandatory for this path by setting min_wrapping_ttl to 1 second.
# This also sets this path's wrapped response maximum allowed TTL to 90 seconds.
path "auth/approle/role/my-role/secret-id" {
capabilities = ["create", "update"]
min_wrapping_ttl = "1s"
max_wrapping_ttl = "90s"
}
If both are specified, the minimum value must be less than the maximum. In addition, if paths are merged from different stanzas, the lowest value specified for each is the value that will result, in line with the idea of keeping token lifetimes as short as possible.
Built-in policies
OpenBao has two built-in policies: default and root. This section describes
the two built-in policies.
Default policy
The default policy is a built-in OpenBao policy that cannot be removed. By
default, it is attached to all tokens, but may be explicitly excluded at token
creation time by supporting authentication methods.
The policy contains basic functionality such as the ability for the token to
look up data about itself and to use its cubbyhole data. However, OpenBao is not
prescriptive about its contents. It can be modified to suit your needs; OpenBao
will never overwrite your modifications. If you want to stay up-to-date with
the latest upstream version of the default policy, simply read the contents
of the policy from an up-to-date dev server, and write those contents into
your OpenBao's default policy.
To view all permissions granted by the default policy on your OpenBao installation, run:
$ bao read sys/policy/default
To disable attachment of the default policy:
$ bao token create -no-default-policy
or via the API:
$ curl \
--request POST \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
--data '{"no_default_policy": "true"}' \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/auth/token/create
Root policy
The root policy is a built-in OpenBao policy that cannot be modified or removed.
Any user associated with this policy becomes a root user. A root user can do
anything within OpenBao. As such, it is highly recommended that you revoke
any root tokens before running OpenBao in production.
When an OpenBao server is first initialized, there always exists one root user. This user is used to do the initial configuration and setup of OpenBao. After configured, the initial root token should be revoked and more strictly controlled users and authentication should be used.
To revoke a root token, run:
$ bao token revoke "<token>"
or via the API:
$ curl \
--request POST \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
--data '{"token": "<token>"}' \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/auth/token/revoke
Managing policies
Policies are authored (written) in your editor of choice. They can be authored in HCL or JSON, and the syntax is described in detail above. Once saved, policies must be uploaded to OpenBao before they can be used.
Listing policies
To list all registered policies in OpenBao:
$ bao read sys/policy
or via the API:
$ curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/sys/policy
Note: You may also see the CLI command bao policies. This is a convenience
wrapper around reading the sys endpoint directly. It provides the same
functionality but formats the output in a special manner.
Creating policies
Policies may be created (uploaded) via the CLI or via the API. To create a new policy in OpenBao:
$ bao policy write policy-name policy-file.hcl
or via the API:
$ curl \
--request POST \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
--data '{"policy":"path \"...\" {...} "}' \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/sys/policy/policy-name
In both examples, the name of the policy is "policy-name". You can think of this name as a pointer or symlink to the policy ACLs. Tokens are attached policies by name, which are then mapped to the set of rules corresponding to that name.
Updating policies
Existing policies may be updated to change permissions via the CLI or via the API. To update an existing policy in OpenBao, follow the same steps as creating a policy, but use an existing policy name:
$ bao write sys/policy/my-existing-policy policy=@updated-policy.json
or via the API:
$ curl \
--request POST \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
--data '{"policy":"path \"...\" {...} "}' \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/sys/policy/my-existing-policy
Deleting policies
Existing policies may be deleted via the CLI or API. To delete a policy:
$ bao delete sys/policy/policy-name
or via the API:
$ curl \
--request DELETE \
--header "X-Vault-Token: ..." \
https://openbao.hashicorp.rocks/v1/sys/policy/policy-name
This is an idempotent operation. OpenBao will not return an error when deleting a policy that does not exist.
Associating policies
OpenBao can automatically associate a set of policies to a token based on an authorization. This configuration varies significantly between authentication backends. For simplicity, this example will use OpenBao's built-in userpass auth method.
An OpenBao administrator or someone from the security team would create the user in OpenBao with a list of associated policies:
$ bao write auth/userpass/users/sethvargo \
password="s3cr3t!" \
policies="dev-readonly,logs"
This creates an authentication mapping to the policy such that, when the user authenticates successfully to OpenBao, they will be given a token which has the list of policies attached.
The user wishing to authenticate would run
$ bao login -method="userpass" username="sethvargo"
Password (will be hidden): ...
If the provided information is correct, OpenBao will generate a token, assign the list of configured policies to the token, and return that token to the authenticated user.
Root protected API endpoints
Note: OpenBao treats the HTTP POST and PUT verbs as equivalent, so for each mention
of POST in the table above, PUT may also be used. OpenBao uses the non-standard LIST HTTP
verb, but also allows list requests to be made using the GET verb along with ?list=true
as a query parameter, so for each mention of LIST in the table above, GET with ?list=true
may also be used.
The following paths requires a root token or sudo capability in the policy:
| Path | HTTP verb | Description |
|---|---|---|
| auth/token/accessors | LIST | List token accessors for all current OpenBao service tokens |
| auth/token/create | POST | Create a periodic or an orphan token (period or no_parent) option |
| pki/root | DELETE | Delete the current CA key (pki secrets engine) |
| pki/root/sign-self-issued | POST | Use the configured CA certificate to sign a self-issued certificate (pki secrets engine) |
| sys/audit | GET | List enabled audit devices |
| sys/audit/:path | POST, DELETE | Enable or remove an audit device |
| sys/auth/:path | GET, POST, DELETE | Manage the auth methods (enable, read, and delete) |
| sys/auth/:path/tune | GET, POST | Manage the auth methods (enable, read, delete, and tune) |
| sys/config/auditing/request-headers | GET | List the request headers that are configured to be audited |
| sys/config/auditing/request-headers/:name | GET, POST, DELETE | Manage the auditing headers (create, update, read and delete) |
| sys/config/cors | GET, POST, DELETE | Configure CORS setting |
| sys/config/ui/headers | GET, LIST | Configure the UI settings |
| sys/config/ui/headers/:name | POST, DELETE | Configure custom HTTP headers to be served with the UI |
| sys/internal/inspect/router/:tag | GET | Inspect the internal components of OpenBao's router. tag must be one of root, uuid, accessor, or storage |
| sys/leases/lookup/:prefix | LIST | List lease IDs |
| sys/leases/revoke-force/:prefix | POST | Revoke all secrets or tokens ignoring backend errors |
| sys/leases/revoke-prefix/:prefix | POST | Revoke all secrets generated under a given prefix |
| sys/plugins/catalog/:type/:name | GET, POST, DELETE | Register a new plugin, or read/remove an existing plugin |
| sys/raw:path | GET, POST, DELETE | Used to access the raw underlying store in OpenBao |
| sys/raw:prefix | GET, LIST | Returns a list keys for a given path prefix |
| sys/remount | POST | Moves an already-mounted backend to a new mount point |
| sys/rotate | POST | Trigger a rotation of the backend encryption key |
| sys/seal | POST | Seals the OpenBao |
| sys/step-down | POST | Forces a node to give up active status |
Tokens
Tokens have two sets of policies: identity policies, which are computed based on the entity and its groups, and token policies, which are either defined based on the login method or, in the case of explicit token creates via the API, are an input to the token creation. What follows concerns token policies exclusively: a token's identity policies cannot be controlled except by modifying the underlying entities, groups, and group memberships.
Tokens are associated with their policies at creation time. For example:
$ bao token create -policy=dev-readonly -policy=logs
Normally the only policies that may be specified are those which are present in the current token's (i.e. the new token's parent's) token policies. However, root users can assign any policies.
There is no way to modify the policies associated with a token once the token has been issued. The token must be revoked and a new one acquired to receive a new set of policies.
However, the contents of policies are parsed in real-time whenever the token is used. As a result, if a policy is modified, the modified rules will be in force the next time a token, with that policy attached, is used to make a call to OpenBao.