Key rotation
OpenBao has multiple encryption keys that are used for various purposes. These keys support rotation so that they can be periodically changed or in response to a potential leak or compromise. It is useful to first understand the high-level architecture before learning about key rotation.
As a review, OpenBao starts in a sealed state. OpenBao is unsealed by providing the unseal keys. By default, OpenBao uses a technique known as Shamir's secret sharing algorithm to split the root key into 5 shares, any 3 of which are required to reconstruct the root key. The root key is used to protect the encryption keyring, which is ultimately used to protect data written to the storage backend.
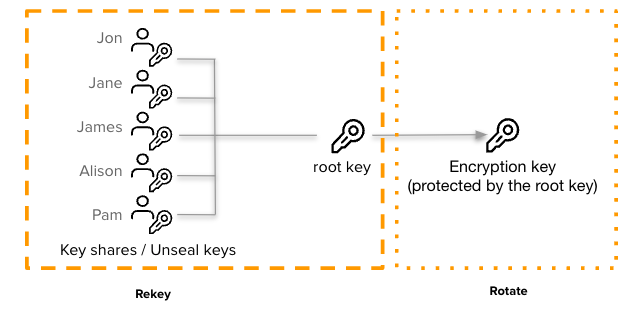
To enable key rotation, we need to support changing the unseal keys, root key, and the backend encryption key.
Note: Historically these actions were split into two separate operations, rekey and
rotate. To further enhance the clarity and address the ambiguity of the terms all
key rotation processes described by the rekey verb were renamed to rotate/<key-name>
instead.
The rotate/root operation is used to generate a new root key. When this is being done,
it is possible to change the parameters of the key splitting, so that the number of shares
and the threshold required to unseal can be changed. To perform a rotation a threshold of
the current unseal keys must be provided. This is to prevent a single malicious operator
from performing a rotation and invalidating the existing root key.
Performing a rotation is fairly straightforward. The rotation must be initialized with the new parameters for the split and threshold. Once initialized, the current unseal keys must be provided until the threshold is met. Once met, OpenBao will generate the new root key, perform the splitting, and re-encrypt the encryption key with the new root key. The new unseal keys are then provided to the operator, and the old unseal keys are no longer usable.
The rotate/keyring operation is used to change the encryption key used to protect data
written to the storage backend. This key is never provided or visible to operators, who
only have unseal keys. This simplifies the rotation, as it does not require the current
key holders unlike the rotate/root operation. When rotate/keyring is triggered, a new
encryption key is generated and added to a keyring. All new values written to the storage
backend would be encrypted with the new key. Old values written with previous encryption
keys can still be decrypted since older keys are saved in the keyring. This allows key
rotation to be done online, without an expensive re-encryption process.
Both the rotate/root and rotate/keyring operations can be done online and in a highly
available configuration. Only the active OpenBao instance can perform either of the
operations but standby instances can still assume an active role after either operation.
This is done by providing an online upgrade path for standby instances. If the current
encryption key is N and a rotation installs N+1, OpenBao creates a special "upgrade"
key, which provides the N+1 encryption key protected by the N key. This upgrade key
is only available for a few minutes enabling standby instances to do a periodic check for
upgrades. This allows standby instances to update their keys and stay in-sync with the
active OpenBao without requiring operators to perform another unseal.
The rotate/keyring/config endpoint is used to configure the number of operations or
time interval between automatic rotations of the backend encryption key.
NIST rotation guidance
Periodic rotation of the encryption keys is recommended, even in the absence of compromise. Due to the nature of the AES-256-GCM encryption used, keys should be rotated before approximately 232 encryptions have been performed, following the guidelines of NIST publication 800-38D.
OpenBao will automatically rotate the backend encryption key prior to reaching 232 encryption operations by default.
Operators can estimate the number of encryptions by summing the following:
- The
vault.barrier.puttelemetry metric. - The
vault.token.creationmetric where thetoken_typelabel isbatch. - The
merkle.flushDirty.num_pagesmetric. - The WAL index.