OpenBao agent and OpenBao proxy
A valid client token must accompany most requests to OpenBao. This includes all API requests, as well as via the OpenBao CLI and other libraries. Therefore, OpenBao clients must first authenticate with OpenBao to acquire a token. OpenBao provides several authentication methods to assist in delivering this initial token.
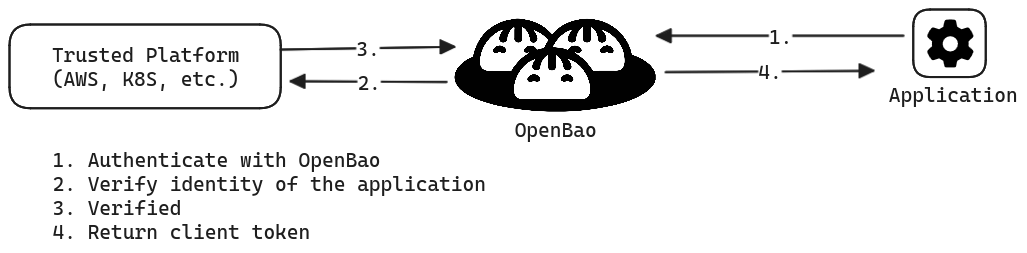
If the client can securely acquire the token, all subsequent requests (e.g., request database credentials, read key/value secrets) are processed based on the trust established by a successful authentication.
This means that client application must invoke the OpenBao API to authenticate with OpenBao and manage the acquired token, in addition to invoking the API to request secrets from OpenBao. This implies code changes to client applications along with additional testing and maintenance of the application.
The following code example implements OpenBao API to authenticate with OpenBao
through AppRole auth method, and then uses
the returned client token to read secrets at kv-v2/data/creds.
package main
import (
...snip...
openbao "github.com/openbao/openbao/api/v2"
)
// Fetches a key-value secret (kv-v2) after authenticating via AppRole
func getSecretWithAppRole() (string, error) {
config := openbao.DefaultConfig()
client := openbao.NewClient(config)
wrappingToken := os.ReadFile("path/to/wrapping-token")
unwrappedToken := client.Logical().Unwrap(strings.TrimSuffix(string(wrappingToken), "\n"))
secretID := unwrappedToken.Data["secret_id"]
roleID := os.Getenv("APPROLE_ROLE_ID")
params := map[string]interface{}{
"role_id": roleID,
"secret_id": secretID,
}
resp := client.Logical().Write("auth/approle/login", params)
client.SetToken(resp.Auth.ClientToken)
secret, err := client.Logical().Read("kv-v2/data/creds")
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("unable to read secret: %w", err)
}
data := secret.Data["data"].(map[string]interface{})
...snip...
}
For some OpenBao deployments, making (and maintaining) these changes to applications may not be a problem, and may actually be preferred. This may be applied to scenarios where you have a small number of applications, or you want to keep strict, customized control over how each application interacts with OpenBao. However, in other situations where you have a large number of applications, as in large enterprises, you may not have the resources or expertise to update and maintain the OpenBao integration code for every application. When third party applications are being deployed by the application, it is prohibited to add the OpenBao integration code.
Introduce OpenBao agent and OpenBao proxy to the workflow
OpenBao Agent and OpenBao Proxy aim to remove this initial hurdle to adopt OpenBao by providing a more scalable and simpler way for applications to integrate with OpenBao. OpenBao Agent can obtain secrets and provide them to applications, and OpenBao Proxy can act as a proxy between OpenBao and the application, optionally simplifying the authentication process and caching requests.
| Capability | OpenBao Agent | OpenBao Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Auto-Auth to authenticate with OpenBao | x | x |
| Caching the newly created tokens and leases | x | x |
| Run as a Windows Service | x | |
| Templating to render user-supplied templates | x | |
| API Proxy to act as a proxy for OpenBao API | Will be deprecated | x |
| Process Supervisor for injecting secrets as environment variables into a process | x |
To learn more, refer to the OpenBao Agent or OpenBao Proxy documentation page.